Mango Network is a next-generation
Layer 1 blockchain that solves the core challenges of fragmentation and liquidity silos in the decentralized world. Unlike traditional blockchains that force developers to choose between the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and high-performance alternatives like MoveVM, Mango integrates both into a single, unified network. As of February 2026, Mango has achieved significant milestones, including a peak throughput of 297,450 TPS and a rapidly growing ecosystem with over 23 million total accounts.
In this article, you will learn what Mango Network is, how its unique Multi-VM technology enables cross-chain communication, the role of the MGO token, why Mango’s modular design is a game-changer for DeFi,
GameFi, and beyond, and how you can trade Mango Network (MGO) on BingX spot and futures markets.
What Is Mango Network (MGO) Multi-VM Infrastructure?
Key features of Mango omni-chain network | Source: Mango Network
Mango Network is an omnichain Layer 1 protocol that functions as a "universal hub" for decentralized applications (dApps). Its primary goal is to provide a secure, modular, and high-performance environment where different virtual machines can coexist and communicate natively. By combining the core advantages of OPStack technology with the Move language, Mango offers a platform that is both highly compatible and mathematically secure.
Mango operates through three technical pillars:
• Multi-VM Support: It natively runs MoveVM, EVM, and
SVM (Solana Virtual Machine) components. This allows developers to deploy Solidity or Move-based contracts on a single chain, which has already attracted over 23.8 million total accounts as of February 2026.
• Omnichain Interoperability: A custom protocol, OP-Mango, enables cross-VM communication. This architecture allows the network to maintain a peak throughput of 297,450 TPS with an average transaction finality of just 380ms, nearly instant compared to traditional L1s.
• Modular Sovereignty: Mango’s architecture separates execution, consensus, and data availability. This separation ensures the network can scale horizontally; while real-world usage averages around 12,000 TPS, the system is designed to handle spikes without the "gas wars" common on monolithic chains, maintaining a reference gas price of approximately 1,000 CELL.
In 2025, Mango successfully transitioned from testnet to mainnet, sparking airdrop mania by distributing 5% of its 10 billion MGO supply or 500 million tokens to early supporters. By early 2026, the network reached a major milestone by integrating a
Bitcoin Layer 2 solution, enabling
BTC assets to interact directly with Mango's DeFi ecosystem, which currently supports over 31,000 daily active users.
How Does Mango Network Work?
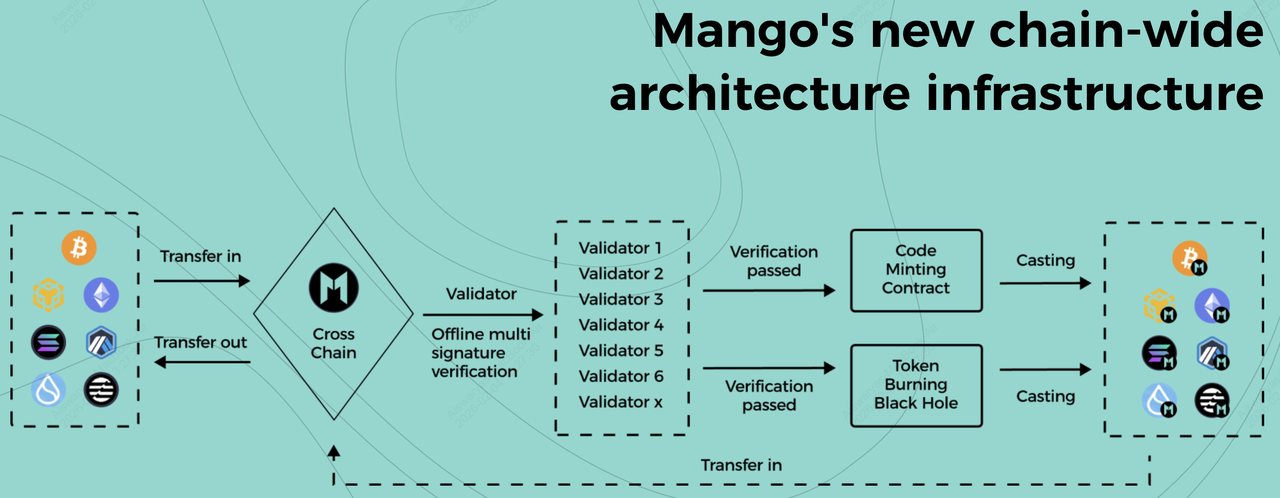
An overview of Mango Network's architecture | Source: Mango Network
Mango Network functions as a Unified Execution Layer, replacing the "isolated" blockchain model with a multi-layered infrastructure that connects heterogeneous networks. By separating transaction dissemination from ordering, Mango ensures it stays fast even under heavy load, achieving a peak throughput of 297,450 TPS with a sub-second finality of approximately 380ms.
1. The Multi-VM Architecture for Parallel Execution at Scale
Mango's "secret sauce" is its ability to run MoveVM, EVM, and SVM (Solana Virtual Machine) in parallel.
• Parallel Scheduling: While traditional chains process transactions one-by-one, Mango’s MoveVM uses a resource-oriented model to dynamically schedule non-conflicting transactions. This allows the network to handle thousands of concurrent operations, maintaining a real-world average of 12,000 TPS without congestion.
• Mathematical Security: By treating digital assets as "first-class resources" via the Move language, Mango eliminates common vulnerabilities like re-entrancy attacks and double-spending at the bytecode level, offering a "safety-first" environment for high-value DeFi.
2. OP-Mango, the Omnichain Communication Protocol
Interoperability is achieved through OP-Mango, a custom cross-VM protocol that acts as a secure data bridge.
• Native Interop: When an event occurs in an EVM contract, e.g., a
Uniswap trade, OP-Mango captures and serializes the data, transmitting it to the MoveVM for settlement.
• Unified State: This enables "hybrid" dApps where a user can use
MetaMask on the EVM front-end while their assets are secured by the high-performance MoveVM back-end, all without leaving the Mango L1.
3. Modular Scaling and the 4 Key Ecosystem Features
Mango is built to scale "out" rather than "up" using a modular design inspired by OPStack.
• Modular Scaling: The network utilizes worker nodes that can be added horizontally. As demand grows, more nodes join the network to increase capacity, keeping gas prices stable at around 1,000 CELL.
• Aggregated Liquidity: Mango’s infrastructure solves the "liquidity silo" problem. Instead of having separate pools on different chains, Mango’s omnichain apps maintain a unified liquidity pool accessible from any supported environment.
• MgoDNS & Identity: The platform provides a decentralized domain service that bridges traditional naming (DNS) with blockchain addresses, simplifying the user experience for its 23.8 million total accounts.
• Bitcoin Layer 2 Integration: Launched in early 2026, this framework uses "isomorphic mapping" to allow BTC assets to be used for on-chain lending and yield farming, bringing the world's largest crypto asset into the Mango DeFi ecosystem.
What Is the MGO Token Used for in Mango Network Ecosystem?
The MGO token is the native utility and governance heart of the Mango Network. With a fixed supply of 10 billion tokens, it aligns the interests of validators, developers, and users.
• Transaction Fees (Gas): MGO is the currency used to pay for all operations across both MoveVM and EVM layers.
• Staking and Security: Validators stake MGO to participate in the Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) consensus. Users can delegate their MGO to earn rewards while securing the network.
• Governance: MGO holders can vote on critical protocol upgrades, the allocation of the Ecosystem Innovation Fund, and parameter changes.
• Ecosystem Incentives: 17% of the supply is dedicated to the Innovation Fund, which provides grants to developers building multi-VM dApps.
What Is MGO Tokenomics?
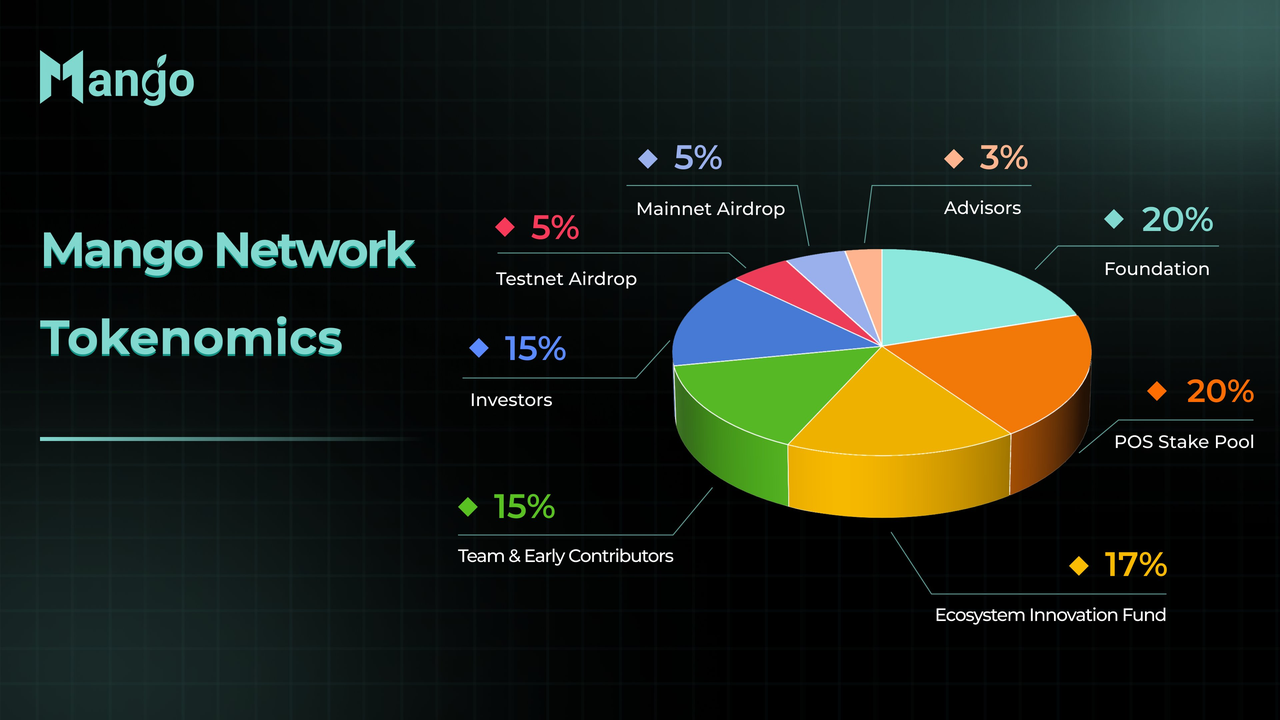
MGO token distribution | Source: Mango Network on X
The MGO token has a fixed maximum supply of 10 billion tokens, designed to sustain the network's security and ecosystem growth through a gradual seven-year unlocking framework.
• POS Stake Pool (20%): 2 billion tokens dedicated to rewarding validators and stakers for securing the network.
• Foundation (20%): 2 billion tokens reserved for research, development, and long-term operational governance.
• Ecosystem Innovation Fund (17%): 1.7 billion tokens progressively released as grants to attract and support developers.
• Team & Early Contributors (15%): 1.5 billion tokens rewarding the core team for building the infrastructure.
• Investors (15%): 1.5 billion tokens allocated to strategic funding partners.
• Community Airdrops (10%): 1 billion tokens split equally between Testnet (5%) and Mainnet (5%) early supporters.
• Advisors (3%): 300 million tokens for strategic guidance and key partnerships.
How to Trade Mango Network (MGO) on BingX
Powered by
BingX AI insights, you can trade MGO with real-time analytics to capitalize on its high volatility and growing market interest using tools like AI Master for strategy optimization.
How to Buy, Sell, or HODL MGO Tokens on the Spot Market
MGO/USDT trading pair on the spot market powered by BingX AI insights
Spot trading is ideal for long-term investors looking to hold the native MGO token in their secure BingX wallet.
• Locate the Pair: Navigate to the
Spot tab and search for the
MGO/USDT trading pair.
• Configure Your Order: Select
Market Order for instant execution at the current price, or Limit Order to specify a target entry price.
• Execute Trade: Enter the amount of
USDT you wish to spend and click Buy MGO to complete the transaction.
How to Trade MGO Futures with Leverage
MGO/USDT perpetuals on the futures market powered by BingX AI insights
For experienced traders, BingX Futures allows you to profit from both rising and falling MGO prices while using leverage to amplify your capital.
• Transfer Funds: Move your USDT from the Funds Account to your Perpetual Futures Account.
• Set Leverage and Margin: Adjust your leverage, e.g., 5x or 10x, and choose between Isolated Margin, which risks only the specific trade, or Cross Margin, which uses total account balance.
3 Key Considerations Before Investing in Mango Network (MGO)
While Mango Network’s technical architecture offers significant advantages in speed and security, investors must balance this potential against the market dynamics and competitive risks inherent to a growing Layer 1 ecosystem.
1. Competitive Layer 1 Landscape: Mango operates in a highly saturated market, competing directly with established high-speed chains like
Sui,
Aptos, and
Monad. Its long-term value depends on its ability to transition from short-term trading momentum, often driven by exchange competitions, to organic developer adoption and a thriving dApp ecosystem.
2. Token Unlock Volatility: As of February 2026, the network is navigating a critical vesting phase. On February 8, 2026, a major unlock of 193.12 million MGO, approximately 12.13% of the circulating supply, is scheduled, which may lead to short-term price fluctuations as early contributors and investors gain liquidity.
3. New Infrastructure Risks: Mango's Multi-VM approach and custom OP-Mango protocol are cutting-edge technologies. While they solve fragmentation issues, they also introduce "novelty risk," where complex cross-VM state synchronizations must remain bulletproof against bugs to maintain user trust and protocol security.
Final Thoughts: Is Mango Network (MGO) a Good Buy in 2026?
Mango Network represents a significant shift toward Chain Abstraction. By removing the barriers between the Move and Ethereum ecosystems, it addresses the "fragmentation" that has held back Web3 adoption for years. With a massive throughput of nearly 300,000 TPS and institutional-grade security via the Move language, it is a strong contender in the infrastructure race.
However, MGO is an infrastructure play, not a "store of value" asset. Its price is tied to the actual usage and volume of the network. If you believe the future of blockchain is omnichain and multi-lingual, Mango Network provides a compelling technical foundation for that vision.
Related Reading