As global regulators tighten oversight on crypto markets and institutions explore tokenization, a key question keeps resurfacing: how can financial assets move
on-chain without exposing sensitive data? This is the problem Dusk Network was built to solve.
Dusk Network is a
Layer-1 blockchain designed specifically for regulated and decentralized finance, combining privacy, compliance, and fast settlement at the protocol level. Instead of retrofitting privacy onto a transparent chain, Dusk embeds
zero-knowledge technology, compliance logic, and institutional-grade finality directly into its core design, a positioning that has recently attracted renewed market attention, with
DUSK posting gains of nearly 400% over the past month alongside a sharp rise in trading volume and investor mindshare.
In this article, you’ll learn what Dusk Network is, how it works under the hood, what makes it different from other
privacy blockchains, and the role of the DUSK token in securing and operating the network.
What Is Dusk Network (DUSK) Layer-1 Blockchain for Privacy?
Dusk Network is a privacy-first Layer-1 blockchain built for real-world financial markets. Its mission is to bring institution-level assets, such as securities, funds, and tokenized real-world assets, on-chain without sacrificing confidentiality or regulatory compliance.
Unlike general-purpose blockchains, Dusk is purpose-built for:
• Confidential transactions
• Programmable compliance
• Instant and final settlement
• Selective auditability for regulators
Dusk serves three core groups:
• Institutions: instant settlement, reduced custodial risk, automated compliance
• Businesses: global liquidity, smart-contract automation, lower operational costs
• Users: self-custody access to regulated financial assets from a wallet
At its core, Dusk removes the traditional divide between “crypto users” and “traditional finance users,” giving both access to the same on-chain financial infrastructure.
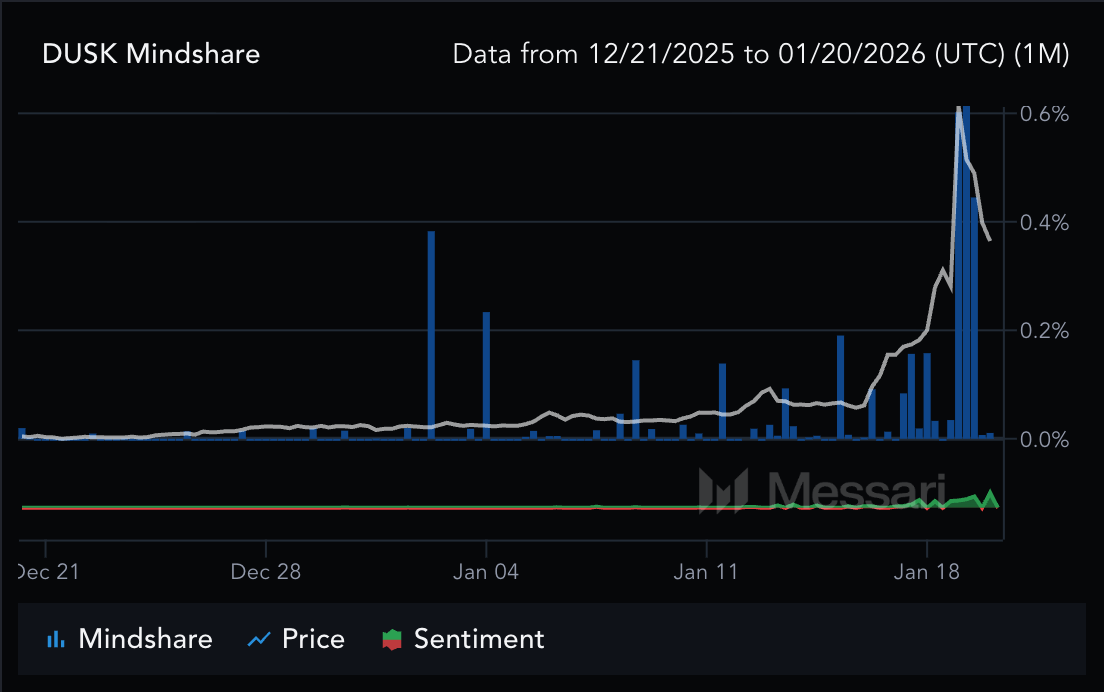
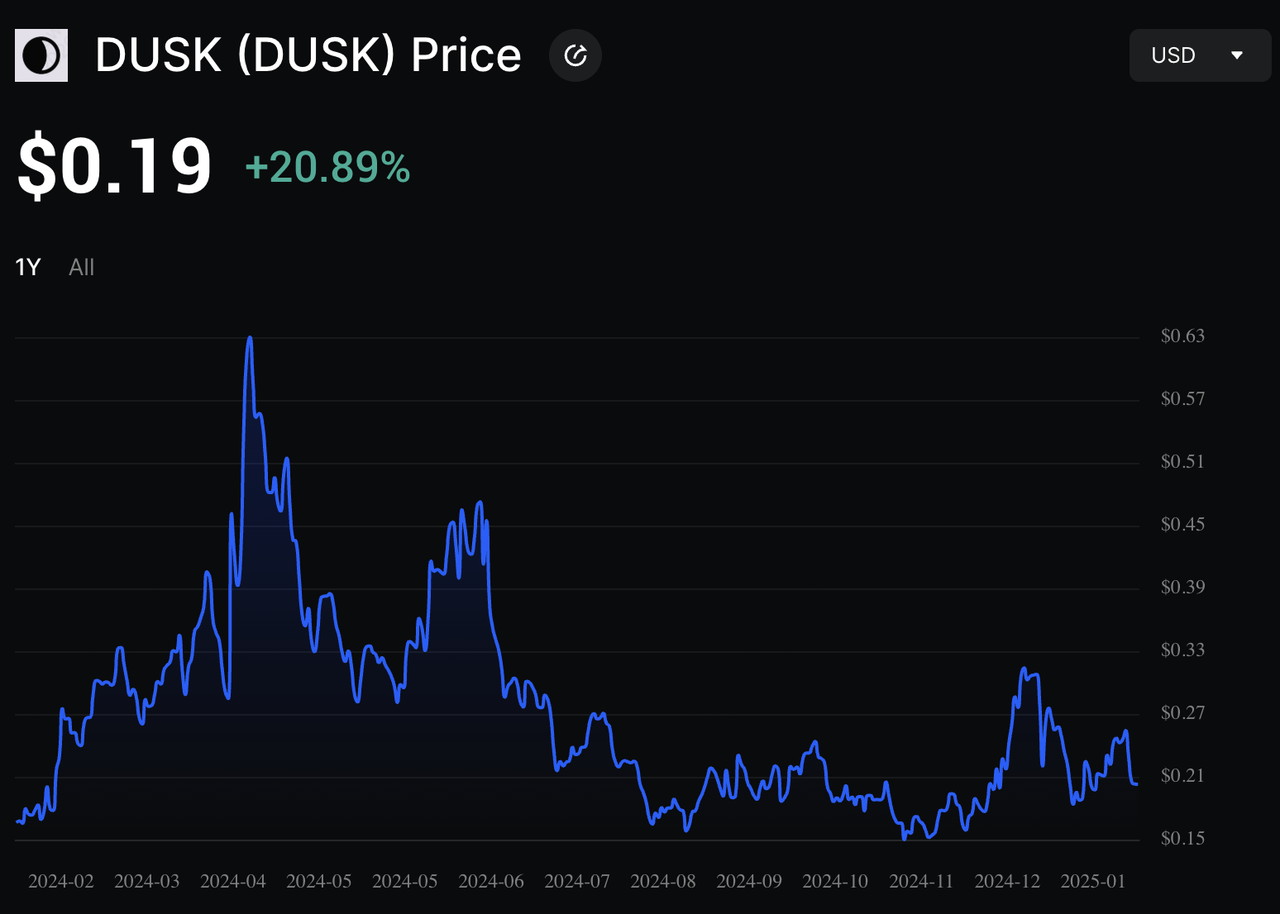
DUSK Price Surges Nearly 400% in January 2026
DUSK price chart on BingX
DUSK has seen sharp short-term volatility alongside strong momentum. As of January 2026,
DUSK is up roughly +167% over the past week and +385% over the past month, lifting its market cap to about $96.7 million. Trading activity has surged, with 24h volume near $207.6 million, giving the tokena Vol/Mkt Cap ratio above 200%, while Messari data shows mindshare up over 1,200% in the last month, signaling rapidly rising attention.
How Does Dusk Network Work?
Dusk’s architecture is modular, combining privacy-preserving execution with deterministic settlement. Each layer is designed to meet the needs of regulated finance.
1. Privacy-Preserving Execution With Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Dusk Network uses zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) as a core execution primitive, allowing the blockchain to verify transactions and smart-contract state transitions without exposing balances, identities, or counterparties on-chain. Instead of validating raw transaction data, the network verifies cryptographic proofs that mathematically guarantee correctness, ensuring ownership, balance integrity, fee payment, and non-double-spending, while keeping sensitive financial information private.
This architecture enables confidential-by-default finance with selective auditability. Institutions and users can transact privately, while regulators or authorized parties can still verify compliance through cryptographic attestations rather than public data disclosure. Unlike privacy add-ons or optional shielding, Dusk enforces privacy at the protocol level, making confidentiality, compliance, and verifiability inseparable parts of how the network executes financial logic.
2. Dual Transaction Model: Moonlight and Phoenix
Dusk Network operates with a dual transaction architecture that allows applications to choose between transparency and confidentiality at the protocol level, rather than forcing a one-size-fits-all model.
i. Moonlight: Account-Based, Transparent
Moonlight is an account-based system similar to
Ethereum, where balances, nonces, and transaction details are publicly visible and easy to audit. This model is well suited for use cases that require full transparency, simple transfers, or straightforward compliance reporting, such as public token movements or basic contract interactions.
ii. Phoenix: UTXO-Based, Privacy-Enabled
Phoenix is a UTXO-based, zero-knowledge transaction model designed for confidential financial activity. It uses cryptographic commitments, nullifiers, and ZK proofs to hide transaction amounts, sender-receiver links, and balance changes while still enforcing ownership, fee payment, and double-spend prevention. Because spent outputs cannot be linked to new ones, Phoenix eliminates transaction tracing and balance leakage, making it suitable for private settlements, regulated securities, and institutional trading strategies.
Together, Moonlight and Phoenix allow Dusk to support transparent compliance flows and privacy-preserving finance on the same blockchain, without fragmentation or external privacy layers.
3. Succinct Attestation Consensus for Fast Finality
Dusk Network secures the chain using Succinct Attestation (SA), a committee-based proof-of-stake consensus designed specifically for financial-grade settlement. Validators (called provisioners) are selected through deterministic, stake-weighted sortition, forming small voting committees for each block. These committees propose, validate, and ratify blocks using BLS aggregated signatures, allowing the network to reach consensus with minimal communication overhead while preserving decentralization. Unlike Nakamoto-style consensus, blocks on Dusk are finalized through explicit cryptographic attestations rather than probabilistic confirmations.
This design enables block finality in seconds, eliminating reorg risk and settlement uncertainty, two critical blockers for on-chain financial instruments. Transactions are not considered “eventually final”; they are deterministically finalized once attested, making them suitable for regulated assets, securities settlement, and institutional clearing workflows. By combining fast finality, predictable settlement outcomes, and capital-efficient PoS security, Succinct Attestation aligns blockchain consensus with the operational requirements of real-world financial markets.
4. Kadcast Network Layer for Efficient Broadcasting
Dusk Network replaces traditional gossip-based networking with Kadcast, a structured peer-to-peer broadcast protocol built on Kademlia-style routing. Instead of flooding messages to all peers, Kadcast forwards blocks, votes, and transactions along deterministic multicast paths based on XOR distance, dramatically reducing redundant transmissions. Research cited in Dusk’s design shows around 25–50% lower bandwidth usage versus gossip protocols, enabling faster and more reliable propagation of consensus messages, especially important when committees exchange frequent votes.
This efficiency translates directly into lower latency and higher reliability under load. By minimizing network congestion, Kadcast helps cut stale/orphaned block rates by 10–30% in fast-block environments, improving effective throughput and consensus stability. Fewer wasted transmissions also reduce CPU and networking overhead across nodes, lowering the network’s energy footprint while maintaining resilience during spikes in activity, an essential property for financial systems that demand predictable performance at scale.
5. Zero-Knowledge Virtual Machine (zkVM)
Dusk Network runs smart contracts on a purpose-built zero-knowledge virtual machine (zkVM) rather than retrofitting privacy onto the EVM. The VM is optimized for native ZK proof verification, confidential state transitions, and financial-grade cryptography, with heavy operations, such as hashing, signature checks, and proof verification, handled through host functions instead of in-VM bytecode. This design avoids the performance penalties seen in generalized WASM or EVM environments, where cryptographic workloads can be 45–250% slower than native execution, and keeps validation deterministic across all nodes.
From a developer perspective, the zkVM enforces a clear separation between private state and public verification. Contracts explicitly define which data remains confidential, which outputs are public, and which compliance conditions must hold. Transactions execute privately, generate a zero-knowledge proof, and then submit only that proof for
on-chain verification. Validators never see the underlying data, yet can cryptographically confirm correctness and rule enforcement. This model allows Dusk to support confidential smart contracts, regulated financial logic, and auditable settlement without relying on trusted execution environments or centralized proof generators.
Is Dusk Network Environmentally Efficient?
Yes. Dusk Network is designed for high energy efficiency, using
proof-of-stake instead of
proof-of-work, which eliminates energy-intensive mining entirely and avoids a hardware arms race. Its Succinct Attestation PoS consensus requires only lightweight validation and committee voting, while the Kadcast network layer reduces bandwidth usage by roughly 25–50% compared to gossip-based protocols, lowering node and infrastructure load.
In addition, Dusk’s virtual machine offloads heavy cryptographic operations, such as zero-knowledge proof verification and signature checks, to native host functions, avoiding the 45–250% performance overhead typical of in-VM execution. Together, these design choices make Dusk significantly more efficient and better suited for always-on, large-scale financial infrastructure than energy-intensive proof-of-work blockchains.
What Are the Real-World Use Cases for Dusk Network?
Dusk Network supports production-grade, regulated financial activity on-chain, combining privacy, compliance, and fast settlement for real economic use cases.
1. Tokenized Equities, Bonds, and Funds: Issue, manage, and transfer regulated financial instruments on-chain with confidential ownership, balance privacy, and deterministic settlement suitable for capital markets.
2. Confidential DeFi and Private Liquidity Pools: Enable trading, lending, and liquidity provision without exposing positions, strategies, or balances, reducing front-running and information leakage for institutions and market makers.
3. Regulated Asset Issuance and Settlement: Automate compliance rules, eligibility checks, and transfer restrictions while achieving near-instant, final settlement without custodians or clearing intermediaries.
4. On-Chain Corporate Actions: Execute dividends, ownership updates, and forced transfers through smart contracts, enforced cryptographically rather than through off-chain reconciliation.
5. Institutional Custody-Free Trading: Allow institutions to trade and settle assets directly from self-custody wallets, minimizing counterparty risk and operational overhead.
Through frameworks like Zedger, Dusk Network supports real financial instruments and compliant market infrastructure, not just experimental DeFi primitives.
What Is the DUSK Token Used For?
DUSK is the native utility token that powers the entire network.
1. Staking and Network Security: Validators, called provisioners, stake DUSK to participate in consensus and earn rewards.
2. Transaction Fees: All transactions, public or private, pay fees in DUSK without exposing sensitive metadata.
3. Smart-Contract Execution: Deploying and interacting with contracts consumes DUSK as gas.
4. Incentives and Penalties: DUSK aligns validator behavior through rewards, slashing, and suspension mechanisms.
5. Governance Participation: Token holders influence protocol upgrades and economic parameters.
DUSK Tokenomics Overview
DUSK has a maximum supply capped at 1,000,000,000 tokens and secures the network using a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism based on Succinct Attestation.
DUSK Rewards Distribution
• 80% to block generators
• 10% to voting committees
• 10% to the protocol treasury
Issuance is designed to support long-term infrastructure security rather than short-term speculation, aligning token value with real network usage.
What Makes Dusk Different From Other Privacy Blockchains?
| Feature |
Dusk Network |
Monero / Zcash |
| Privacy |
Default, programmable |
Transaction-level |
| Compliance |
Built into protocol |
External / limited |
| Smart contracts |
Confidential by design |
Limited |
| Settlement finality |
Deterministic |
Probabilistic |
| Institutional focus |
Yes |
No |
Dusk Network takes a selective and programmable approach to privacy, rather than enforcing blanket anonymity across all activity. Privacy is applied at the transaction and smart-contract level, allowing developers to define what data stays private, what is revealed publicly, and what can be disclosed conditionally. This enables confidential balances, counterparties, and trading logic, while still supporting cryptographic proofs for auditability, reporting, and compliance when required.
Most privacy blockchains prioritize anonymity above all else, which limits their usability in regulated environments. Dusk is designed specifically for regulated financial markets, embedding compliance logic directly into the protocol through zero-knowledge proofs, deterministic finality, and rule-enforced smart contracts. Regulators and institutions can verify that rules were followed, such as eligibility, ownership, or transfer restrictions, without accessing raw transaction data.
As a result, Dusk positions privacy as a functional feature for real finance, not an ideological stance against oversight. This makes it suitable for use cases like tokenized securities, institutional DeFi, and compliant asset settlement, areas where anonymity-only chains struggle to gain adoption.
How to Trade DUSK on BingX Futures
DUSK/USDT perpetual contract on the futures market powered by BingX AI
With
BingX AI-powered trading tools, you can trade DUSK futures using leverage, advanced risk controls, and AI-assisted insights designed for volatile markets.
1. Fund your account: Deposit or transfer USDT to your BingX Futures wallet.
2. Open Futures Market: Go to
Futures → USDT-M Perpetuals and search for
DUSK/USDT.
3. Choose leverage: Select leverage carefully (lower leverage reduces liquidation risk).
4. Set order type: Pick
Market or Limit, then choose Long (price up) or Short (price down).
Reminder: Futures trading involves leverage and carries higher risk. Always size positions responsibly and understand
liquidation mechanics before trading.
Final Thoughts
Dusk Network is focused on a specific problem: enabling privacy-preserving financial activity that can operate within real regulatory frameworks. Rather than optimizing for maximum transparency or pure anonymity, it combines zero-knowledge proofs, fast deterministic finality, and programmable compliance to support regulated assets, confidential settlement, and institutional-grade on-chain workflows.
As tokenization and institutional participation continue to expand, blockchains that balance privacy, compliance, and decentralization are likely to become increasingly relevant infrastructure. That said, adoption depends on factors such as regulatory clarity, ecosystem growth, and real-world usage. As with all crypto assets and networks, participation in the Dusk ecosystem involves market, technical, and regulatory risks, and outcomes may vary as conditions evolve.
Related Reading