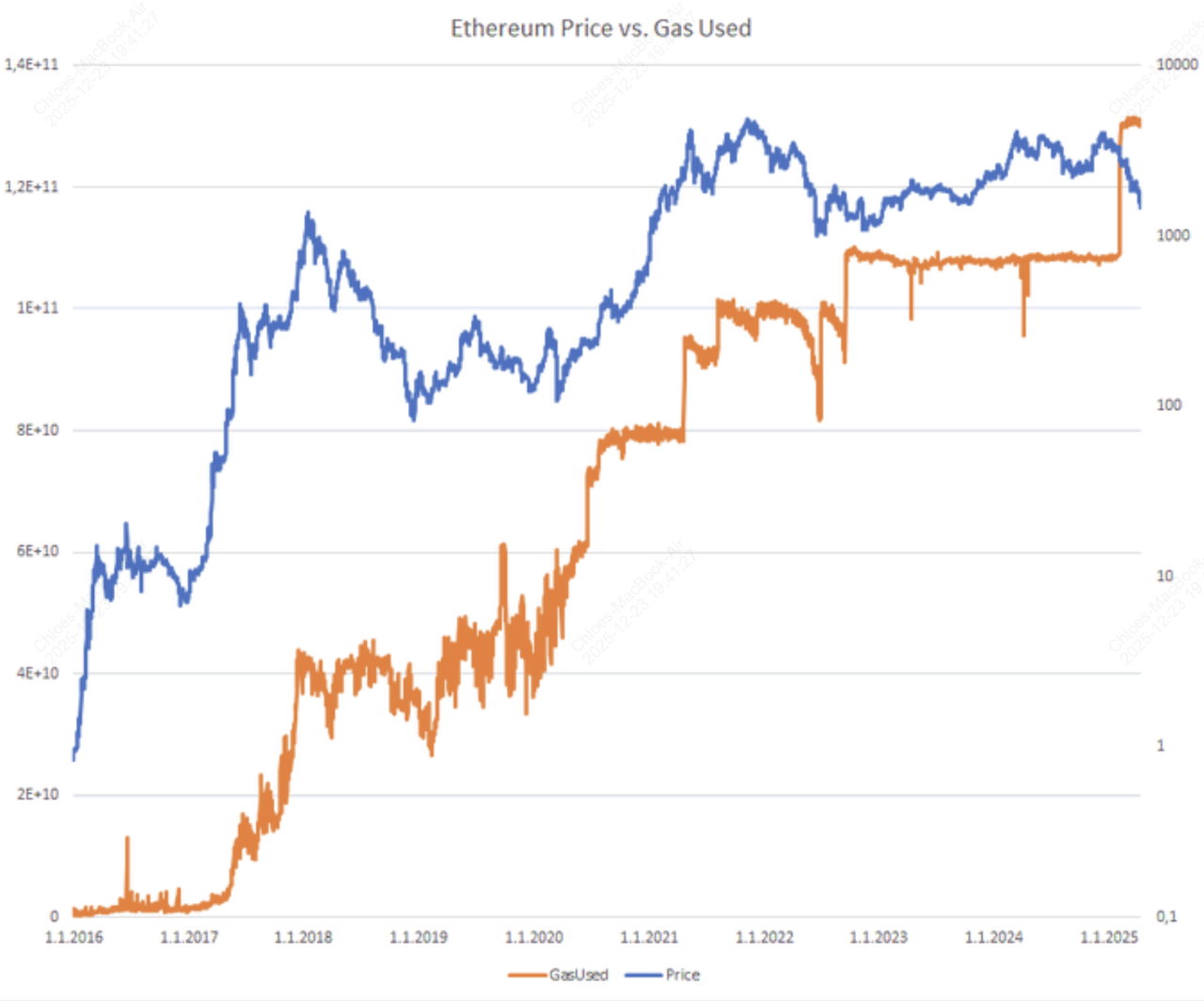
Ethereum (ETH) stands as the world's leading smart contract platform in 2025, hosting a vast ecosystem of
decentralized finance (DeFi),
NFTs, gaming, and real-world assets with over $166 billion in total value locked (TVL) across its mainnet and
Layer-2 solutions. The network processes approximately 1.7 million transactions daily, supported by more than 35 million
staked ETH securing its proof-of-stake consensus. Yet, every interaction requires payment of
gas fees, denominated in Gwei, to compensate validators for processing and securing the blockchain.
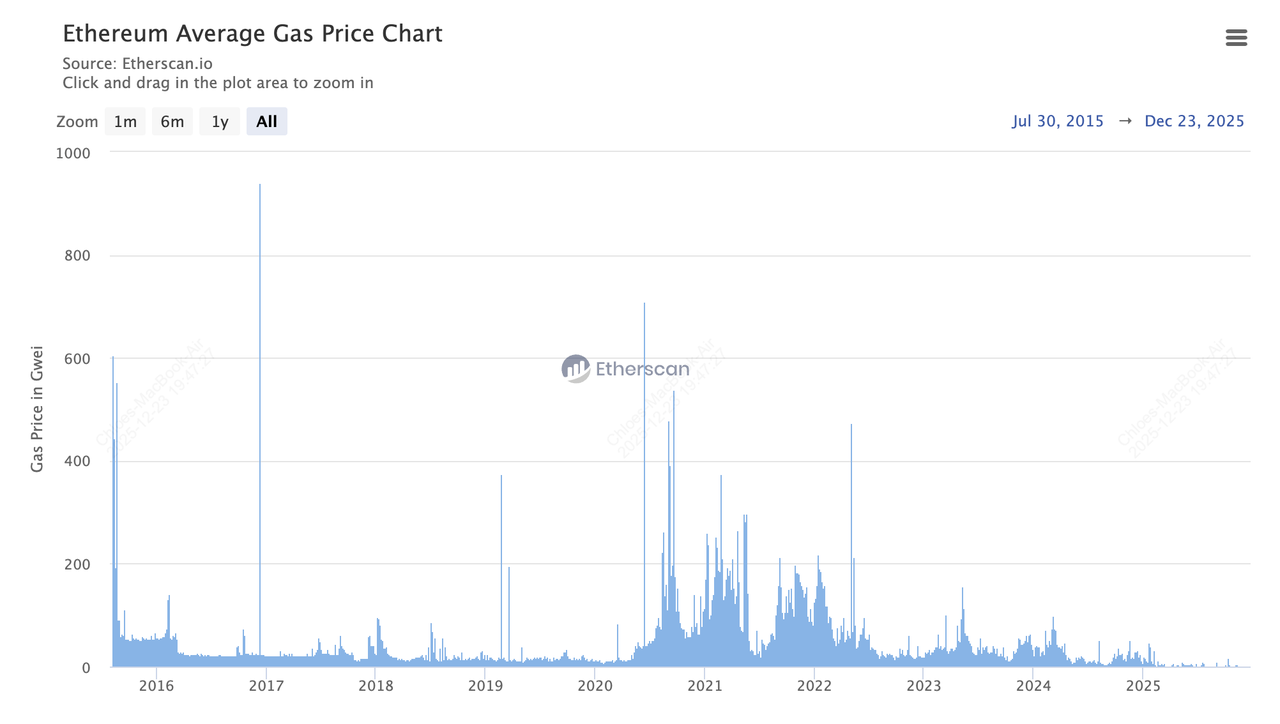
As of December 2025, current gas prices hover at extremely low levels around 0.034 Gwei, making simple transfers cost mere cents, a stark contrast to historical peaks. The transformative 2024 Dencun upgrade slashed average fees by up to 95%, dropping from over 70 Gwei pre-upgrade to sustained lows below 3 Gwei throughout much of 2025, while
Layer 2 networks now handle the majority of activity with fees often under $0.01. This beginner's guide explores the essentials of
ETH gas and Gwei, backed by up-to-date facts, figures, and strategies to help newcomers navigate Ethereum's fee system efficiently amid its ongoing evolution toward greater scalability and affordability.
What Is Ethereum Gas?
Ethereum gas represents the computational effort required to execute operations on the blockchain, acting as a metering system to allocate resources fairly among users. Every action, whether sending ETH, executing a smart contract, or minting an NFT, consumes a certain amount of gas units, which are then multiplied by the current gas price to determine the total fee paid in ETH.
For instance, a simple ETH transfer typically requires 21,000 gas units, while more complex interactions like token swaps on
Uniswap can demand 30,000 to 150,000 units or more, ensuring the network remains secure and resistant to spam by making frivolous transactions uneconomical.
What Is Gwei and What Does 1 Gwei Mean?
Gwei, short for gigawei, is a subunit of Ethereum's native cryptocurrency, ETH, where 1 Gwei equals 0.000000001 ETH, or one billionth of an ETH, making it a convenient denomination for expressing small transaction fees without dealing with excessive decimal places. This unit is named after Wei, the smallest ETH denomination (1 ETH = 1Q Wei), so 1 Gwei is equivalent to 1,000,000,000 Wei, providing precision for gas pricing in everyday use.
For context, if ETH is priced at $2,000, 1 Gwei would be worth about $0.000002, highlighting how even modest Gwei values can add up in high-volume or complex transactions, though in late 2025's low-fee environment, totals remain minimal.
How ETH Gas Prices are Measured in Gwei
Gas prices on Ethereum are primarily measured in Gwei per gas unit, allowing users to set how much they're willing to pay for each unit of computational work, with higher prices incentivizing faster processing by validators. Following the EIP-1559 upgrade in 2021, gas prices consist of a base fee automatically adjusted by the network based on demand and an optional priority fee or tip, where the base fee is burned to reduce ETH supply, contributing to deflationary pressure. Historical data shows average gas prices fluctuating wildly, from lows of 10-30 Gwei for standard transfers during quiet periods to peaks over 200 Gwei during network congestion, but in 2025, averages have stabilized below 3 Gwei post-Dencun, with current snapshots as low as 0.034 Gwei.
What Are Ethereum Gas Fees and How Do They Work?
Ethereum gas operates through a system where users specify a gas limit the maximum units they're willing to consume and a gas price in Gwei, with the actual fee calculated as gas used multiplied by the effective gas price, ensuring transactions only proceed if sufficient gas is provided.
This mechanism is vital because it rewards validators for their work, prevents denial-of-service attacks by making spam costly, and maintains the network's decentralization and efficiency, as without gas, malicious actors could overload the system with infinite loops or junk data.
In 2025, with Ethereum's capacity expanded through sharding and Layer 2 solutions handling up to 1.9 million daily transactions, gas remains a cornerstone, handling billions in daily transaction value while adapting to growing adoption.
Why Are ETH Gas Fees So High?
ETH gas fees are the total costs incurred for processing transactions on the Ethereum network, paid in ETH but often quoted in Gwei, and they can seem exorbitantly high due to factors like network congestion, where demand exceeds the blockchain's limited block space, forcing users to bid higher for inclusion.
Factors influencing these fees include transaction complexity simple transfers cost less than intricate smart contract executions overall network demand during peak times like market volatility or NFT drops, and the fixed block size that creates competition among users.
Even after upgrades, fees have averaged around 50-100 Gwei in busy periods historically, though the
2024 Dencun upgrade slashed costs by 95% on average, with late 2025 mainnet fees often under $0.10 for simple transfers, making Ethereum more accessible yet still variable based on real-time activity.
How to Read Gwei Values on Wallet Confirmations
When confirming a transaction in wallets like
MetaMask or Trust
Wallet, Gwei values appear as the gas price per unit, often categorized into low (under 1 Gwei in current conditions for slower processing), average, or high, alongside the total estimated fee in ETH and fiat equivalents.
Source: Etherscan
Users can interpret these by noting the base fee (network-determined) and adding any tip, with tools like Etherscan or wallet estimators providing real-time Gwei trackers and
on-chain analysis to help decide if the displayed value aligns with current market conditions, ensuring you don't overpay or risk delays.
For example, a confirmation showing 0.034 Gwei might yield a total fee of under $0.01 for a 21,000-unit transfer in December 2025.
Top Tips to Reduce Your Ethereum Gas Fees
If you trade or transfer assets on Ethereum, using the right strategies can significantly lower transaction costs, often without affecting execution quality.
1. Trade during off-peak hours: Transact late at night or on weekends (UTC), when network activity typically drops, which can reduce gas fees by up to 50% compared with peak periods.
2. Use Layer-2 networks: Leverage solutions like
Arbitrum or
Optimism, which batch transactions off-chain and account for over 60% of Ethereum activity in 2025, often bringing effective fees down to a fraction of mainnet costs.
3. Batch transactions where possible: Combining multiple actions into a single transaction reduces repeated base fees and lowers the cost per action.
4. Set custom gas prices: Use gas estimators such as ETH Gas Station to avoid overpaying, and choose slower confirmation speeds when urgency is low.
5. Consider alternative blockchains: Networks like
Polygon offer similar smart-contract functionality at significantly lower fees than Ethereum mainnet.
Tip: In 2025, traders who combine smart timing, Layer-2 usage, and gas monitoring tools like
Etherscan commonly report 50–90% savings on transaction fees compared with peak-hour Ethereum mainnet transactions.
How to Buy Ethereum on BingX
Purchasing Ethereum directly on centralized exchanges like BingX allows users to acquire ETH without incurring on-chain gas fees, as these platforms handle internal transfers off the blockchain, offering a cost-effective entry point compared to decentralized exchanges where swaps involve high Gwei prices during congestion.
ETH/USDT trading pair on the spot market powered by BingX AI insights
1. Create or log in to your BingX account: Sign up with your email or mobile number and
complete KYC if required in your region.
3. Go to Spot Trading: Open the Spot Market and search for
ETH/USDT
4. Use BingX AI for market insights: Check AI-generated signals, market trends, and price analysis to make informed decisions before placing your trade.
5. Enter the amount of ETH you want to buy: Choose
Market Order for instant execution or Limit Order to set your preferred price.
6. Confirm your purchase: Review your order, tap Buy, and your ETH will be added to your BingX Spot Wallet.
7. Store or transfer your ETH tokens: Keep your ETH securely on BingX or withdraw to a self-custody wallet for DeFi, staking, or Web3 apps.
Conclusion
In summary, ETH gas and Gwei form the backbone of Ethereum's fee structure, ensuring fair resource allocation while adapting to technological advancements that have made the network more efficient and affordable in 2025, with fees at historic lows and Layer 2 driving mass adoption. By grasping these concepts from basic calculations to influencing factors and applying practical tips, beginners can confidently engage with Ethereum, minimizing costs and maximizing the benefits of this innovative blockchain ecosystem powering billions in value daily. As Ethereum continues to evolve, staying informed through reliable trackers and updates will be key to navigating its dynamic fee landscape.
Related Reading